Index
OOP
is an approach to the solution of problems in which all computations are performed in the context of objects.
Object
Instance of class
Chunk of structured data in a running SW system
Has properties that represent its state
Has a behavior:
- how it acts and reacts.
- may simulate the behavior of an object in the real world.
- It exists and is instantiated (created) from a data type created with class keyword
Class
Unit of abstraction in an object oriented program
Represent similar objects: its instances.
A kind of SW module
- describes its instances' structure (properties)
- contains methods to implement their behavior.
the code is organized using classes, each of which describes a set of objects
A class is a logical abstraction.
Identity
Each object is distinct from each other object.
Two objects are different even if they have the same data.
Encapsulation
Wrapping of data and functions into a single unit (called class)
Data is not accessible to outside world
Only wrapped functions can access that Data.
Functions provide interface between the object's data and the program.
Abstraction
Act of representing the essential features without including background details and explanations.
Classes use the concept of abstraction and are defined as a list of attributes and functions (methods) that operate on these attributes.
The concept of abstraction also relates to the idea of hiding data that are not needed for presentation
Polymorphism
An abstract operation that may be performed in different ways in different classes.
Multiple methods with the same name
The choice of which execute depends on the calling object.
Polymorphism is the mechanism by which several methods can have the same name and implement the same abstract operation.
More details about abstraction here.
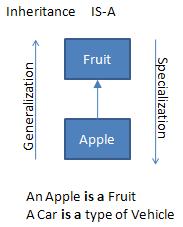
Inheritance
Objects of one class acquire the properties of objects of another class
Reusability (add additional features to an existing class without modifying it)
The derived class shares common characteristics with the class from which it is derived
The implicit possession by all subclasses of features defined in its superclasses.
Inheritance is the mechanism where feautres in a hierarchy inherit from superclasses to subclasses.
Superclasses
Contain features common to a set of subclasses
Inheritance Hierarchies
Show relationship among superclasses and subclasses
A triangle show generalization:
Abstract classes and Methods
An operation should be declared to exist at the highest class hierarchy when it makes sense.
The operation may be abstract (lacking of implementation) at that level.
If so, the class must be abstract:
- no instances can be created.
- the opposite of an abstract class is a concrete class
If a superclass has an abstract operation then its subclasses at some level must have a concrete mothod for the operation:
- Leaf classes must have or inherit concrete methods for all operations.
- Leaf classes must be concrete.
Dynamic Binding
Aka Late Binding
This is a form of polimorphism.
Is the way to determine the exact implementation of a request based on both the request (operation) and the receiving object at run-time.
Is invoking a derived class member function using a pointer to its base class.
The implementation of the derived class will be invoked instead of that of the base class.
Dynamic Dispatch
virtual
Mapping a message to a specific sequence of code (method) at runtime.
This is done to support th cases where the appropriate method cannot be determined at compile time (statically).
Dynamic dispatch is only used for code invocation and not for other binding processes (like global variables)
Namespaces
Creates a declaration region in which various program elements can be placed.
Help in the organization of large programs.
You can create sub-namespaces or create super-namespaces by joining other namespaces.
I understand this concepts as Sets of names (identifiers) common to an application.
BOOL
New data type defined in C++
It only have two values: true, false.
true corresponds to int 1, and false match int 0.
General Form of Class Declaration
class className {
private data and functions
public:
public data and functions
} object namelist;
Operator Overloading
Detailed information here. This link is interesting because shows how to avoid problems when assigning an object to itself.
Documentation above do not include ++ and --, this is included here. This is very simple, check the following bullets:
Restrictions:
- Can not alter precedence
- Can not change the number of operands
- Except for the function call operator ( ), no other operator can have default arguments
- The following operators can not be overloaded:
Generalization vs. Specialization
Both refer to the same: something is a something else
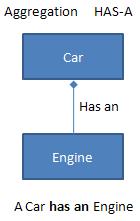
Aggregation
A class/object contains another class/object as its member